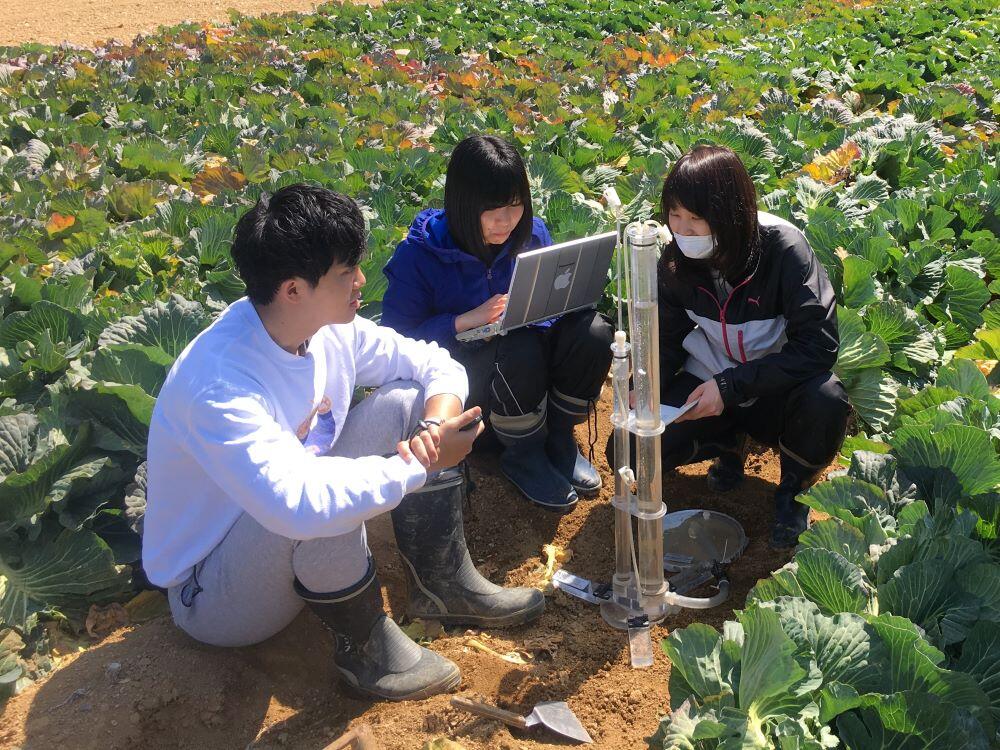
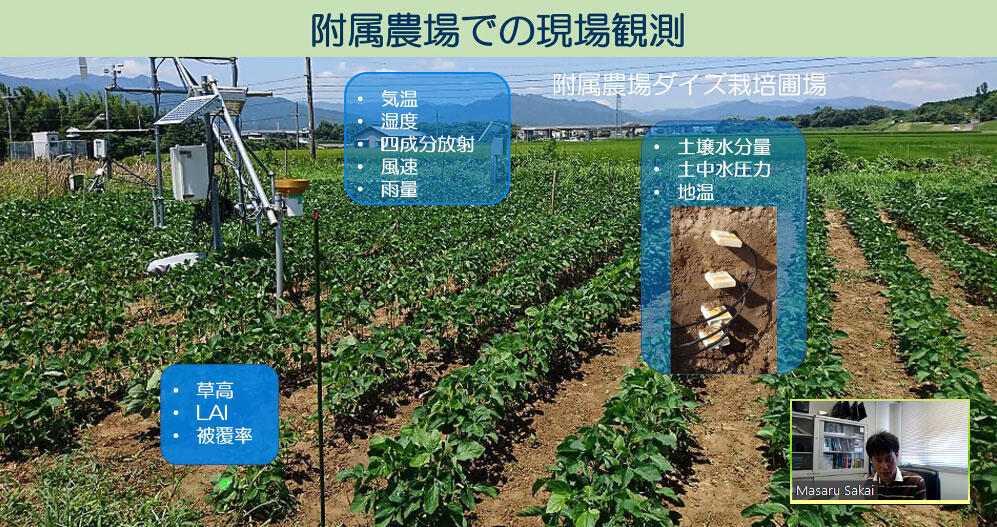
The vadose zone, also termed the unsaturated zone, is a soil layer from the surface to the position of the groundwater, generally corresponding to the plant root zone. Unsaturated water flow, solute, heat, and gas transport with the carbon and nitrogen cycling in the vadose zone are experimentally and numerically studied. Field and laboratory experiments are conducted to intensively monitor water flow and solute transport. Numerical simulation models are developed to predict water, heat, and chemical transport with plant root uptake in a soil including nitrogen components in a solution phase and carbon dioxide in a gas phase as a result of degradation of organic matters. Furthermore, the chemical transport model is applied to predict cesium transport in agricultural fields of Fukushima area.